CS3 In the News
MIT Joint Program Deputy Director C. Adam Schlosser offers his perspective on local, regional and global climate trends (Boston Globe)
Launched in 2017 in France, the Energy Observer operates as a mobile clean energy laboratory and as a demonstration of its onboard technologies (Boston Globe)
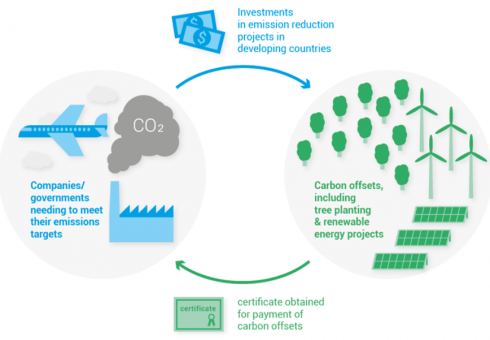
“Clean energy” usually refers to energy sources that produce no climate-warming greenhouse gas emissions in their operation. That doesn’t mean they have zero impact on the environment. (MIT Climate Portal)
The balance of phytoplankton populations in the sea is shifting as a result of human-induced climate change, altering the oceans in profound ways (BBC)
Behind the headlines, evidence points to an industry continuing to grow and innovate (Christian Science Monitor)
MIT Joint Program Deputy Director Sergey Paltsev shares his perspective on the TILclimate podcast (MIT Climate Portal)
So said MIT Joint Program Deputy Director Sergey Paltsev in a presentation at the April 10-11 Wings of Change Americas conference in Santiago, Chile (Litoral Press, Spanish)
New version incorporates last four years of climate knowledge (MIT Environmental Solutions Initiative)
MIT Joint Program Research Scientist Angelo Gurgel shares his expertise as a guest on the Anti-Dread Climate Podcast (NPR/KCRW)
This measure, developed by MIT researchers, reflects direct effects on people’s quality of life — and reveals significant global disparities (MIT News)
Supply-side restrictions, like shutting down new oil wells or gas pipelines, tend to lead to more imports and minimal impacts on greenhouse gas emissions—unless paired with other policies that limit demand for fossil fuels (MIT Climate Portal)
As part of the new Climate Project at MIT, the center will create and strengthen connections between leading climate researchers and policymakers (MIT Sloan School of Management) (Coverage: Boston Globe, Axios, MIT Technology Review)