EPPA Model Structure
The general framework is a multi-sector, multi-region, computable general equilibrium (CGE) model of the world economy. It utilizes the GTAP dataset (maintained at Purdue University) that includes input-output relationships among sectors within a broader social accounting matrix that includes exports, imports, government, investment and household demand for final goods, and the ownership and supply to each sector of labor, capital and natural resources.
The standard economic specification of the model in billions of dollars of inputs (capital rents, labor, resource rents) and outputs (gross output of each sector and output supplied to each final demand sector) is augmented with accounts in physical terms on energy (exajoules), emissions (tons), land use (hectares), population (billions of people), natural resource endowments (exajoules, hectares) and efficiencies (energy produced/energy used) of advanced technology.
These supplemental physical accounts translate economic accounts (in billions of dollars) to corresponding estimates of physical depletion and use of natural resources, technical efficiencies of energy conversion processes and against limits of annual availability of renewable resources such as land availability, and the number of people affected to consider health effects.
Major goals:
- Energy, economy, GHG and air pollutant projections
Representation:
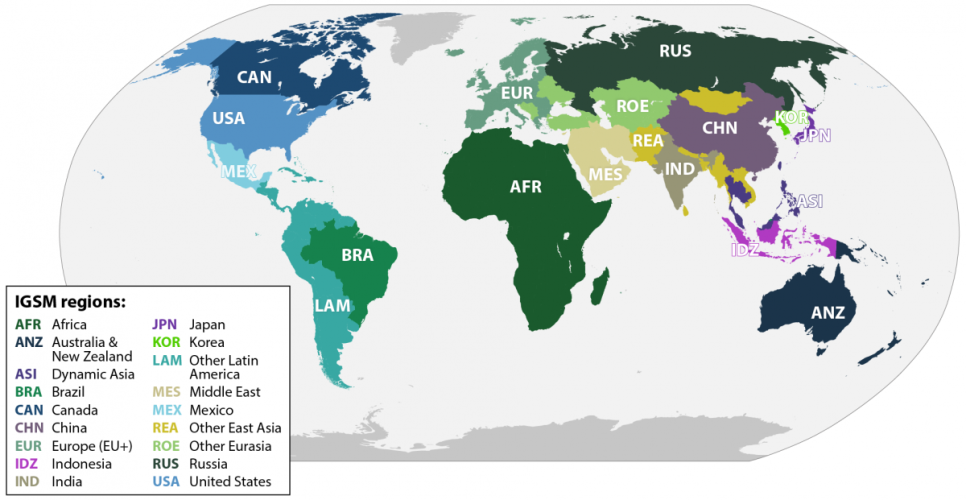
- Global coverage
- All sectors of economy
Model Features:
- Theory-based
- Prices are endogenous
- International trade
- Inter-industry linkages
- Distortions (taxes, subsidies, etc.)
- GDP and welfare effects
Trade-off:
- Aggregated representation of regions, sectors, technologies
Expansion:
- Industrial CCS options
- Hydrogen production options
- Hydrogen pathways
- Direct air capture
- CO2 utilization pathways
| Non-Energy Sectors | |
|---|---|
| Crops | |
| Livestock | |
| Forestry | |
| Food | |
| Energy-Intensive Industry | Iron & Steel |
| Non-Metallic Minerals (Cement, etc.) | |
| Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, etc.) | |
| Petrochemicals (Fertilizers, Olefins, etc.) | |
| Manufacturing | |
| Industrial Transport | |
| Household Transport | ICE (Gasoline & Diesel) |
| Plug-in Electric | |
| Battery Electric | |
| Hydrogen | |
| Energy Sectors | |
|---|---|
| Crude Oil | |
| Refined Oil | |
| Liquid Fuel from Biomass | Current Generation |
| Advanced Biofuels | |
| Oil Shale | |
| Coal | |
| Natural Gas (conv., shale, tight, CBM) | |
| Electricity | Coal |
| Natural Gas | |
| Oil | |
| Advanced Gas | |
| Advanced Coal | |
| Coal with CCS | |
| Coal + Bio Co-firing with CCS | |
| Gas with CCS | |
| Gas with Advanced CCS | |
| Nuclear | |
| Advanced Nuclear | |
| Hydro | |
| Solar | |
| Wind | |
| Wind with Backup | |
| Solar with Backup | |
| Biomass | |
| Biomass with CCS | |
| Synthetic Gas (from coal) | |
For special projects, sectoral and regional disaggregation can be expanded.
